8 Courses
-
A Romp Through Ethics for Complete Beginners
-

A Romp Through Ethics for Complete Beginners (1/7)
-

A Romp Through Ethics for Complete Beginners (2/7)
-

A Romp Through Ethics for Complete Beginners (3/7)
-

A Romp Through Ethics for Complete Beginners (4/7)
-

A Romp Through Ethics for Complete Beginners (5/7)
-

A Romp Through Ethics for Complete Beginners (6/7)
-

A Romp Through Ethics for Complete Beginners (7/7)
-
-
Critical Reasoning for Beginners
-
Critical Reasoning for Beginners
-
D.H. Lawrence
-
General Philosophy
-

1.1 An Introduction to General Philosophy
-

1.2 The Birth of Modern Philosophy
-

1.3 From Aristotle to Galileo
-

1.4 The Birth of the Early Modern Period: From Galileo to Descartes
-

2.1 Recap of General Philosophy
-

2.2 Introduction to Thomas Hobbes
-

2.3 Robert Boyle's Corpuscularian Theory
-

2.4 Isaac Newton and Instrumentalism
-

2.5 Introduction to John Locke
-

2.6 George Berkeley and Idealism
-

3.1 Introduction to David Hume
-

3.2 David Hume: Concluding Remarks
-

3.3 The Problem of Induction
-

4.1 Scepticism of the External World
-

4.2 Possible Answers to Scepticism of the External World
-

4.3 Introduction to Cartesian Dualism
-

4.4 Modern Responses to Dualism
-

5.1 Introduction to Knowledge
-

5.2 The Traditional Analysis of Knowledge
-

5.3 Gettier and Other Complications
-

5.4 Skepticism, Externalism and the Ethics of Belief
-

6.1 Introduction to Primary and Secondary Qualities
-

6.2 Problems with Resemblance
-

6.3 Abstraction and Idealism
-

6.4 Making Sense of Perception
-

7.1 Free Will, Determinism and Choice
-

7.2 Different Concepts of Freedom
-

7.3 Hume on Liberty and Necessity
-

7.4 Making Sense of Free Will and Moral Responsibility
-

8.1 Introduction to Personal Identity
-

8.2 John Locke on Personal Identity
-

8.3 Problems for Locke's View of Personal Identity
-

8.4 Persons, Humans and Brains
-
-
Old English in Context
-
Quantum Mechanics
-

Introduction to Quantum Mechanics, Probability Amplitudes and Quantum States
-

Dirac Notation and the Energy Representation
-

Operators and Measurement
-

Commutators and Time Evolution (the Time Dependent Schrodinger Equation)
-

Further TDSE and the Position Representation
-

Wavefunctions for Well Defined Momentum
-

Back to Two-Slit Interference, Generalization to Three Dimensions and the Virial Theorem
-

The Harmonic Oscillator and the Wavefunctions of its Stationary States
-
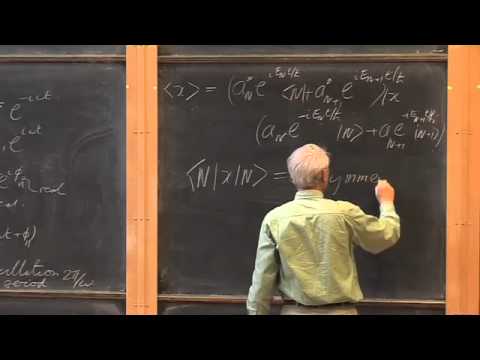
Dynamics of Oscillators and the Anharmonic Oscillator
-

Transformation of Kets, Continuous and Discrete Transformations and the Rotation Operator
-

Transformation of Operators and the Parity Operator
-

Angular Momentum and Motion in a Magnetic Field
-

Hilary: The Square Well
-

A Pair of Square Wells and the Ammonia Maser
-

Tunnelling and Radioactive Decay
-

Composite Systems - Entanglement and Operators
-

Einstein-Podolski-Rosen Experiment and Bell's Inequality
-
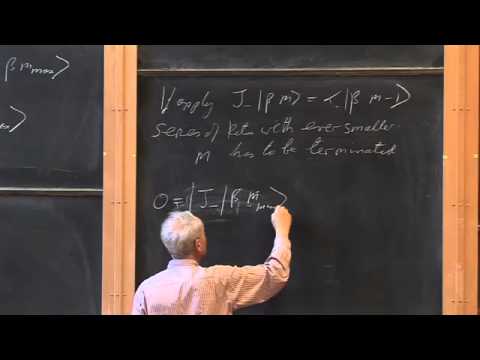
Angular Momentum
-

Diatomic Molecules and Orbital Angular Momentum
-
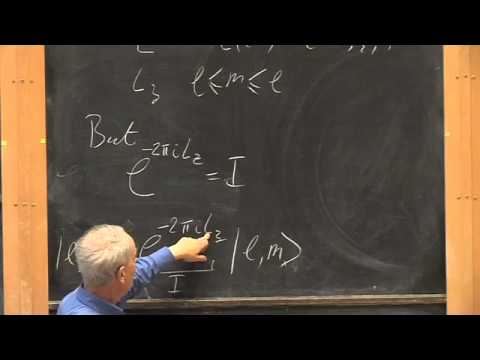
Further Orbital Angular Momentum, Spectra of L2 and LZ
-
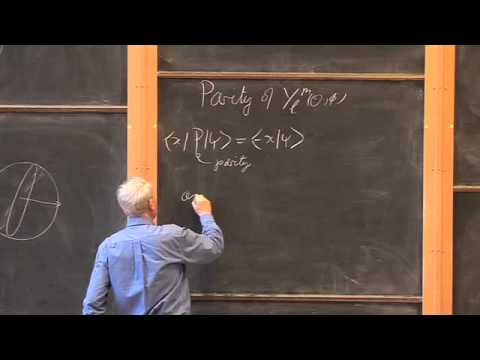
Even Further Orbital Angular Momentum - Eigenfunctions, Parity and Kinetic Energy
-

Spin Angular Momentum
-

Spin 1/2 , Stern - Gerlach Experiment and Spin 1
-
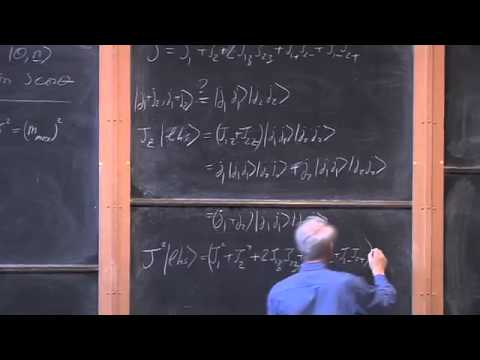
Classical Spin and Addition of Angular Momenta
-

Hydrogen part 1
-

Hydrogen part 2 Emission Spectra
-

Hydrogen part 3 Eigenfunctions
-
-
The Elements of Drawing




























